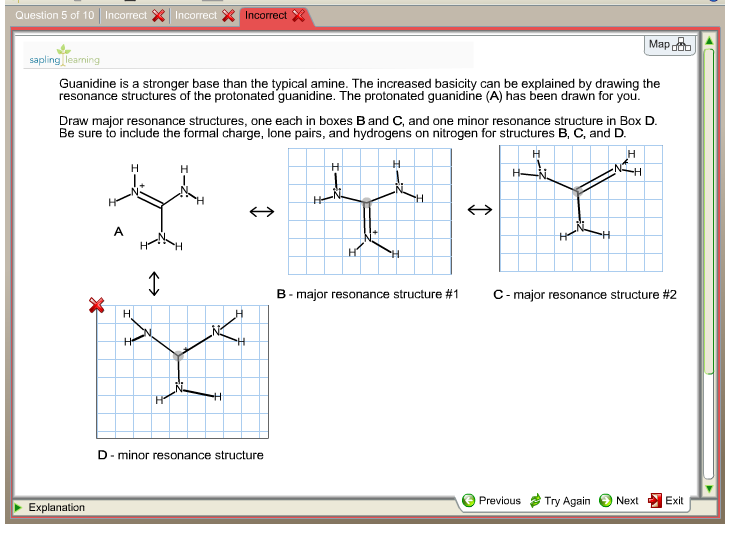
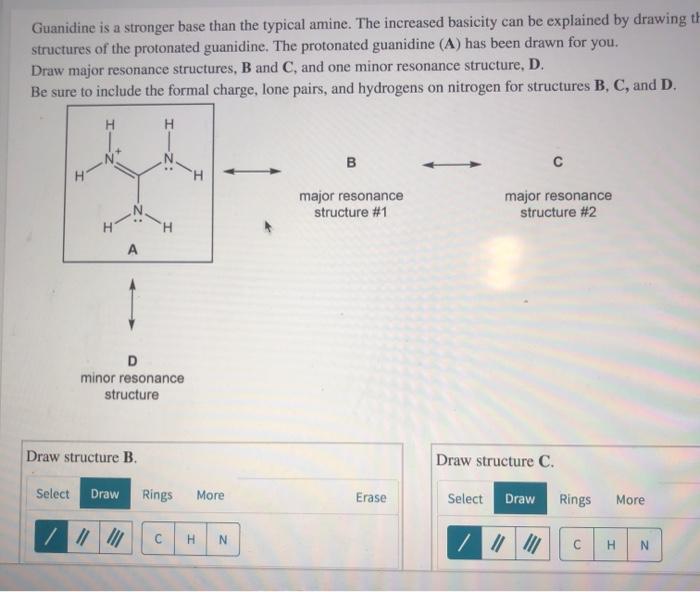
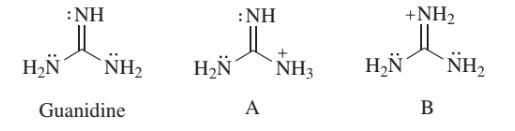
Guanidine is a stronger base than the typical amine The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for youPLAYLIST is at web site wwwdigitaluniversityorg Read "Guanidinium‐Type resonance stabilization and its biological implications I the guanidine and extended‐guanidine series, Journal of Computational Chemistry" on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips

Synthesis And Coordination Of A Neutral Phosphaguanidine And Comparison Of Its Basicity With A Guanidine
Guanidine resonance structures
Guanidine resonance structures-Guanidine is isolobal to urea, where the carbonyl oxygen has been replaced by an imine $\ce{NH}$ However, in principle it is still the same flat, resonancestabilised molecule The main difference is that there is no 'preferred' site for the double bond — it could point towards any of the three nitrogens in theory;Resonance structures of guanidine I have learned about the octet rule, and I saw in some examples that it is however possible for a Catom to only have 6 electrons around him (like in pyridin ) So when i tried to calculate the Resonace structures of guanidine, I wondered why there must be 8 electrons around C this time (like this video )




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Give An Explanation For The Fact That Guanidine Nh C Ch3 2 Is A Stronger Base Than Most Of Amines
Chloride, Guanidinium Chloride, Guanidium Guanidine Guanidine Hydrochloride Guanidine Monohydrate Guanidine Monohydrobromide Guanidine MonohydrochlorideYou could say the diamide resonance is enhancedAn unusual type of πelectron delocalization in Yshaped molecules related to guanidine and its protonated form, the guanidinium ion, has been studied by ab initio methods at the STO3G and 3
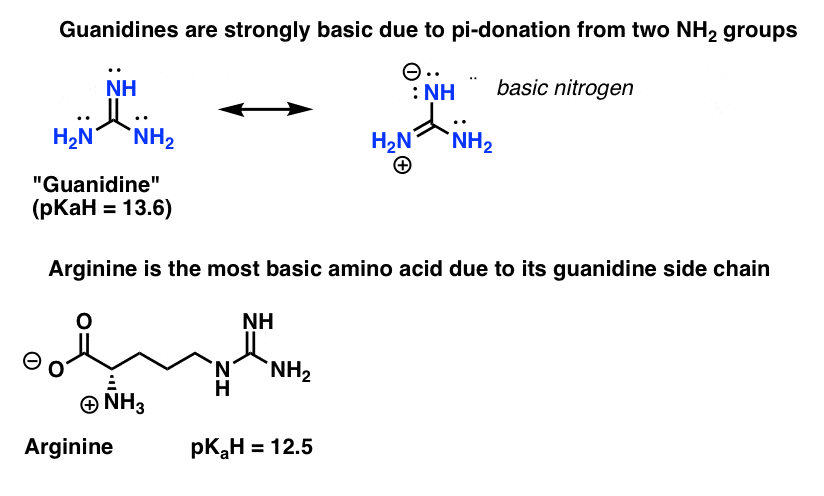
This is caused by resonance between the three structures which can be written by allotting the positive charge to each of the three nitrogen atoms in turn The resonance energy is the cause of the stability of the ion and hence of the strong basic character of the compoundHowever, such a presentation of the guanidine molecule gives an insight into the chemical properties of guanidine derivatives, featuring both nucleophilic and electrophilic characters 2However, contrary to Oja, we observed the low frequency pair to have about twice the intensity of the high frequency pair
Of two possible structures A and B for the conjugate acid of guanidine, the more stable is the one that is better stabilized by electron delocalization Which one is it?Guanidine is a stronger base than the typical amine The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for youQ The conjugate acid of guanidine has 3 equivalent resonance structures, along with one other canonical structure, and is therefore rather highly resonance



2




Protonation Of Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange
Formal presentation of the guanidine structure (a) and the resonance structures of its protonated form (b) Obviously, this is only formal consideration;Guanidine is an aminocarboxamidine, the parent compound of the guanidines It is a onecarbon compound, a member of guanidines and a carboxamidineIt is a conjugate base of a guanidinium Guanidine is resonancestabilized, which means it should be less basic than methylamine Methylamine would be more reactive/nucleophilic/basic because comparatively it lacks any resonance stabilization



Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine Chegg Com




File Guanidiniumion Mesomerie Svg Wikimedia Commons
Guanidine Acetate, C(NHZ)3CH3C00 Four resonance frequencies were observed at 77 K and at 295 K Our frequency values agree closely with those determined by Oja (7);Q One contributing resonance structure to a resonance hybrid is given Curved arrows are used to show how electron pairs move to generate a second reson



Ch 610b




Guanidine Formula Uses Facts Britannica




Organic Chemistry Video 17 Resonance Example 13 Guanidine Youtube



1




Synthesis And Coordination Of A Neutral Phosphaguanidine And Comparison Of Its Basicity With A Guanidine
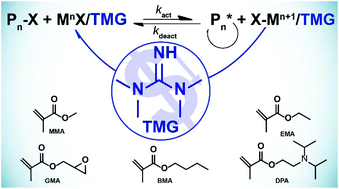



Guanidine As Inexpensive Dual Function Ligand And Reducing Agent For Atrp Of Methacrylates Polymer Chemistry Rsc Publishing




Ppt Organic Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



1



Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine Chegg Com
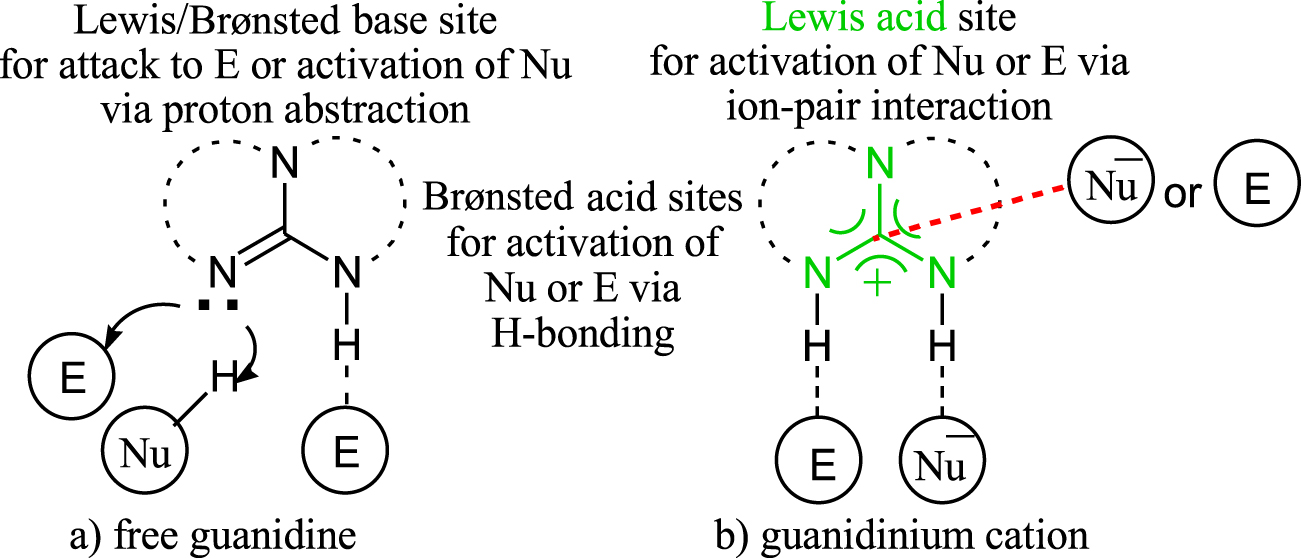



New Insights Into The Lewis Acidity Of Guanidinium Species Lewis Acid Interaction Provides Reactivity



Guanidine Wikiwand



2




Z0eg3zaa3wsvem




Basicity Of Guanidines With Heteroalkyl Side Chains In Acetonitrile Eckert Maksic 08 European Journal Of Organic Chemistry Wiley Online Library




Synthesis And Properties Of Three Guanidinium Salts Based On High Oxygen Balanced 1 4 Dinitramino 3 5 Dinitropyrazolate Anion Sciencedirect




With Aid Of Resonance Structures Show That Proton Transfer To Guanidine Occurs Preferentially To Its Nh B Than Its Nh 2 A Groups Study Com




Bestand Guanidinium Ion Canonical Forms 2d Skeletal Png Wikipedia




Problems And Answers On Acidity And Basicity 13 Chemistry Guider




Synthesis And Properties Of Novel Guanidine Bases N N N Tris 3 Dimethylaminopropyl Guanidine Sciencedirect




Guanidine Hydrochloride




Suggested Structures For The Co Mn Br Guanidine Catalyst System M M Download Scientific Diagram



Answered Nh Nh Nh2 Nh2 Nh3 H N Nh2 Bartleby




27 1 Amino Acids Proteins Chapter A Amino Acids Amino Acid Amino Acid A Compound That Contains Both An Amino Group And A Carboxyl Ppt Download
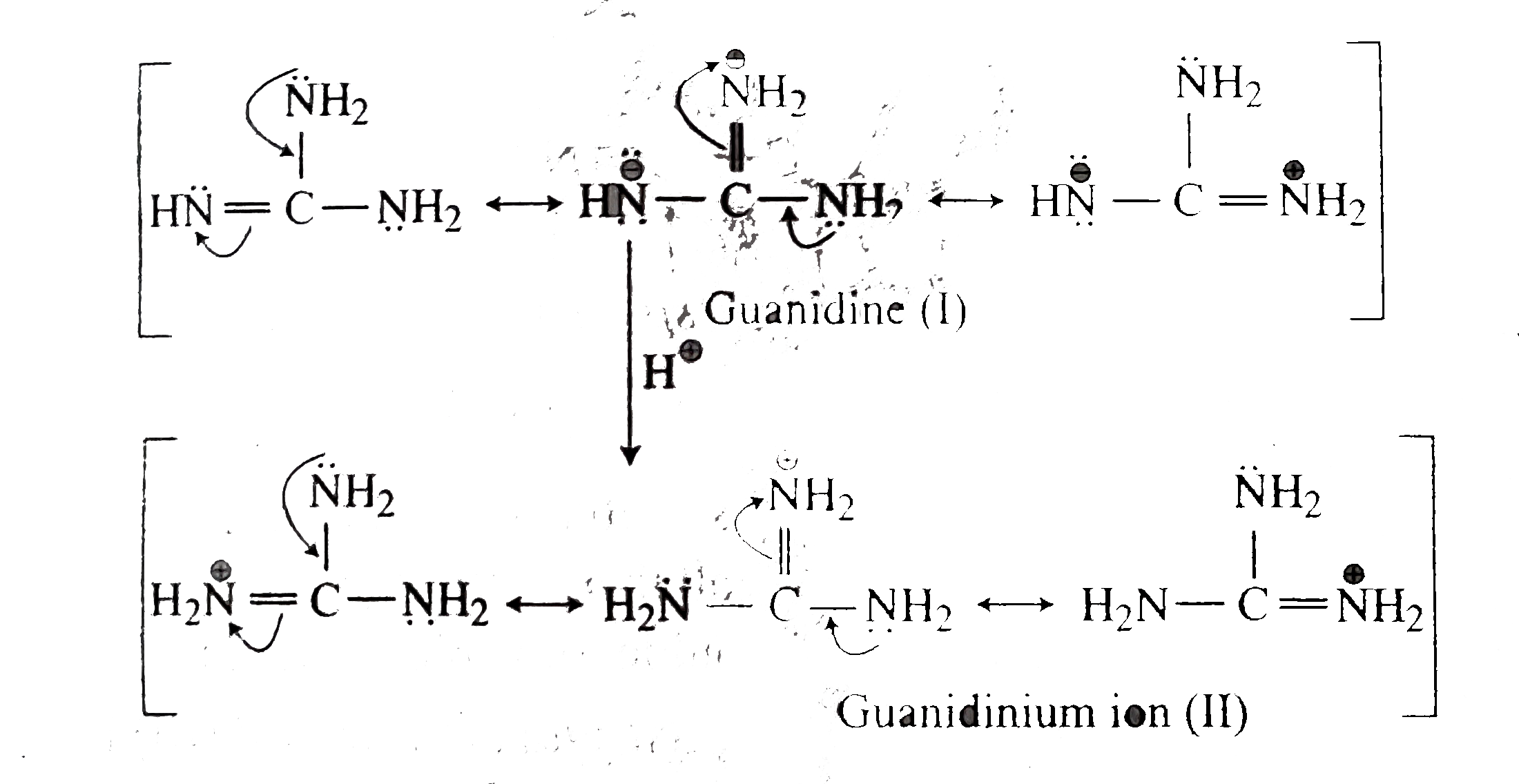



Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely To Be Protonated



5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry
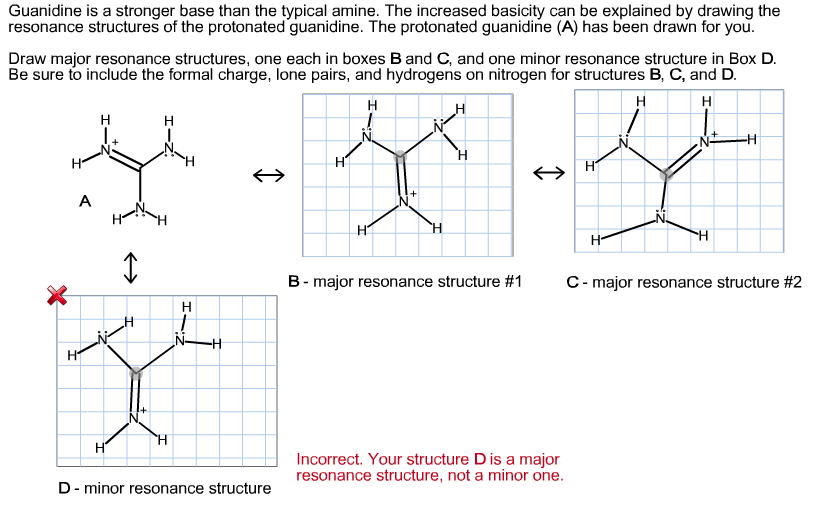



Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine Chegg Com




With Aid Of Resonance Structures Show That Proton Transfer To Guanidine Occurs Preferentially To Its Nh B Than Its Nh 2 A Groups Study Com




Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine The Increased Basicity Can Be Explained By Brainly Com




Modified Guanidines As Chiral Auxiliaries Ishikawa 02 Chemistry A European Journal Wiley Online Library




Synthesis And Properties Of Alkyl Bis Guanidinium Acetates Surfactants




Introduction Of The Guanidine Functionality To A Dendrimer S Peripheral Download Scientific Diagram



Guanidine Sulfamate 1 1 13c Nmr Spectrum Spectrabase
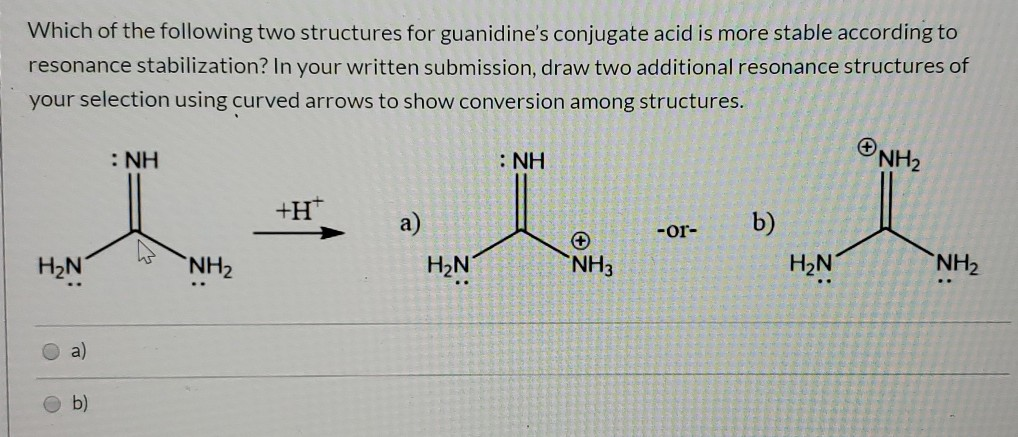



Solved Which Of The Following Two Structures For Guanidine S Chegg Com




Part 17 Guanidine Amidine Pyridine Pyrrole Basicity Applications Of Resonance Nishant Sir Youtube
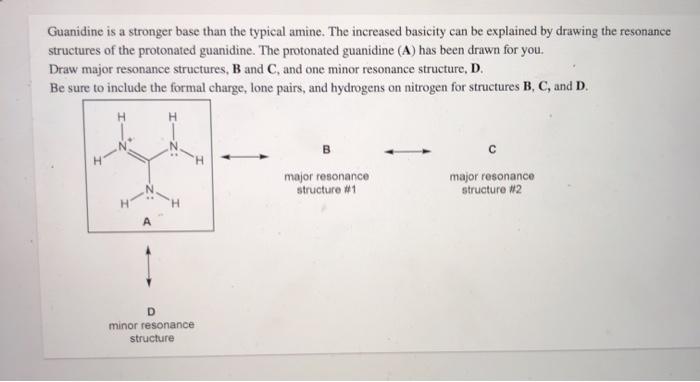



Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine Chegg Com




Epb1 Methods For The Synthesis Of Polycyclic Guanidine Compounds Google Patents




Figure 1 4 From I The Synthesis And Coordination Chemistry Of Novel 6pi Electron Ligands Ii Improvement Of Student Writing Skills In General Chemistry Lab Reports Through The Use Of Calibrated Peer Review




Unusual Oxidative Chemistry Ofn W Hydroxyarginine And N Hydroxyguanidine Catalyzed At An Engineered Cavity In A Heme Peroxidase Sciencedirect




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Give An Explanation For The Fact That Guanidine Nh C Ch3 2 Is A Stronger Base Than Most Of Amines
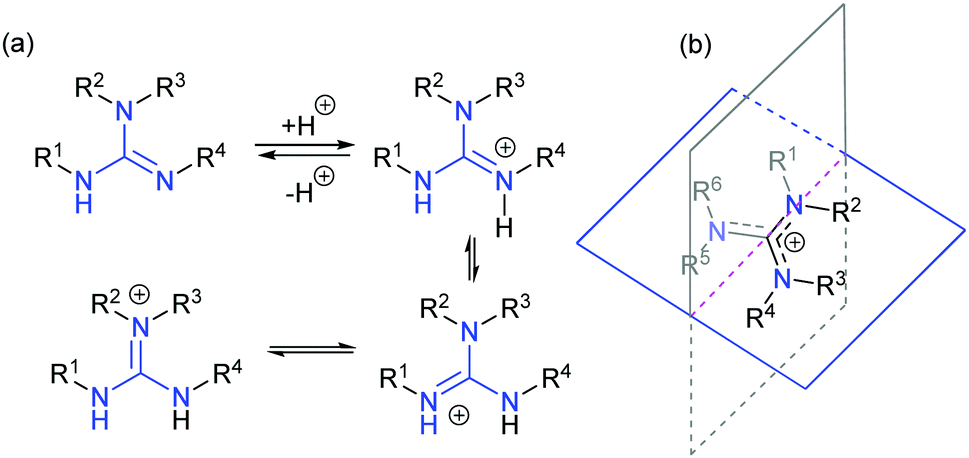



Chiral Guanidines And Their Derivatives In Asymmetric Synthesis Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing




Figure 1 10 From Comparison Of Silica Based Poly Amine Containing Ion Exchangers And Their Guanidine Derivatives For Selective Pgm Recovery From Authentic Refinery Process Solutions Semantic Scholar




File Guanidine 2d Png Wikipedia




Guanidine Is A Neutral Compound But Is An Extremely Powerful Base In Fact It Is Almost As Strong A Brainly Com




Of Two Possible Structures A And B For The Clutch Prep




Mixed Amido Imido Guanidinato Niobium Complexes Synthesis And The Effect Of Ligands On Insertion Reactions Dalton Transactions Rsc Publishing



1



Solved Guanidine Pka 13 6 Is A Very Strong Base Almost As Basic As Hydroxide Ion A Complete




File Guanidinium Ion 2d Skeletal Png Wikimedia Commons




Amines The Organic Bases Categorizing Amines Amines Are Categorized By The Number Of Alkyl Groups Attached To Nitrogen 1º Primary Amine Rnh 2 2º Secondary Ppt Download



Solved Draw Structures For Each Of The Following Functional Groups At Ph 4 Provide Resonance Forms When Appropriate A Hydroxyl B Carboxyl C Imi Course Hero



Guanidine Derivative Polymer Coated Microbubble Resonator For High Sensitivity Detection Of Co2 Gas Concentration




Protonation Of Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange
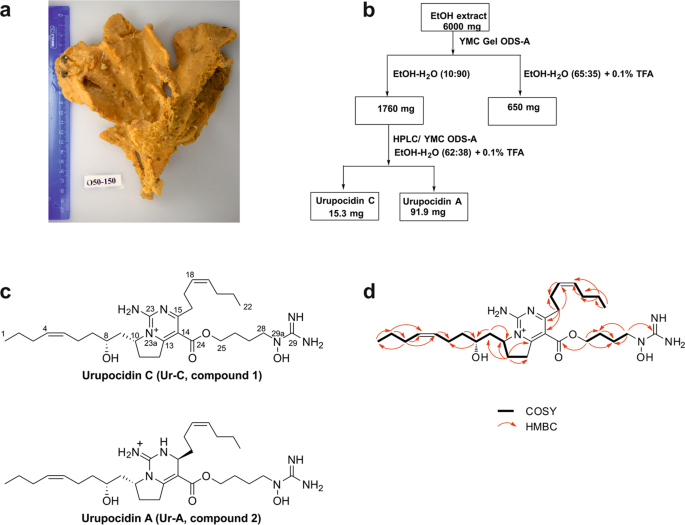



Urupocidin C A New Marine Guanidine Alkaloid Which Selectively Kills Prostate Cancer Cells Via Mitochondria Targeting Scientific Reports
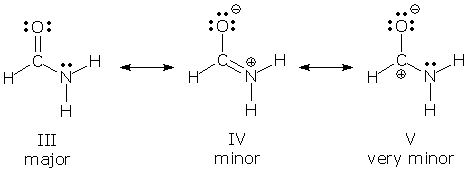



Roco Resonance Major Minor




How To Solve These Problems 1 C Sony 2 Hani Nh2 One Has A Stronger Homeworklib




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Give An Explanation For The Fact That Guanidine Nh C Ch3 2 Is A Stronger Base Than Most Of Amines




Iit Jee Guanidine Ammidine In Hindi Offered By Unacademy




Guanidine Wikipedia



Guanidine A Simple Molecule With Great Potential From Catalysts To Biocides And Molecular Glues



Guanidine A Simple Molecule With Great Potential From Catalysts To Biocides And Molecular Glues




Amines The Organic Bases Categorizing Amines N Amines



2




Of Two Possible Structures A And B For The Clutch Prep
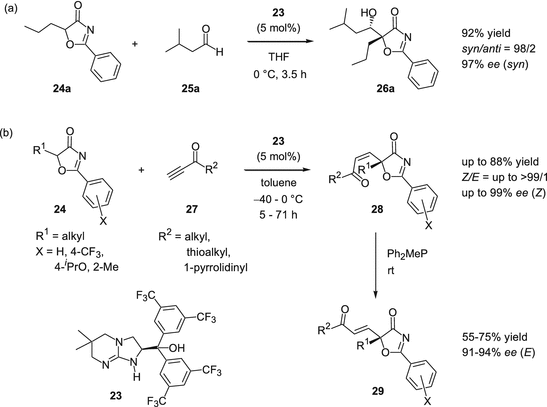



Bifunctional Guanidine Hydroxide And Related Organocatalysts Springerlink




Protein Structure




Which Nitrogen Is Prtonated Redily In The Guanidine




100以上 Guanidine Resonance Structures Guanidine Resonance Structures Tanfreepicta
/63589E4AF83B1572802585F9006F4B6A/$file/FG09296_structure.png)



Guanidine Hcl 50 01 1 Biosynth Carbosynth



Chemical Forums Resonance And Basicity



Which Is The Most Basic Nitrogen In Guanidine Quora




Multinuclear Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Is Used To Determine Rapidly And Accurately The Individual Pka Values Of 2 Deoxystreptamine Neamine Neomycin Paromomycin And Streptomycin Acs Omega X Mol




Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely To Be Protonated
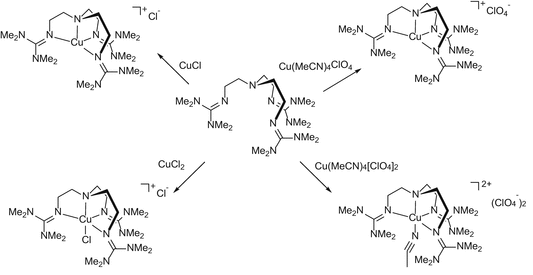



Guanidine Metal Complexes For Bioinorganic Chemistry And Polymerisation Catalysis Springerlink




Syntheses And Crystal Structures Of Guanidine Hydrochlorides With Two Schiff Base Functions As Efficient Colorimetric And Selective Sensors For Fluoride



Py421 Week Two Review And Study Guide
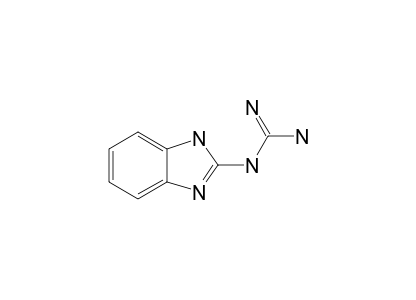



N 2 Benzimidazolyl Guanidine 13c Nmr Spectrum Spectrabase




Vive 119 Guanidine Is Among The Strongest Neutral Base Nh Hnnh Guanidine The Reason For The




Synthesis And Coordination Of A Neutral Phosphaguanidine And Comparison Of Its Basicity With A Guanidine



Exam 3 Answer Key




Scheme 2 Reversible Protonation Of Guanidine In The Presence Of Co 2 Download Scientific Diagram




Guanidine Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia




Role Of Arginine Guanidinium Moiety In Nitric Oxide Synthase Mechanism Of Oxygen Activation Journal Of Biological Chemistry




Protonation Of Guanidine Why Is The Sp2 Nitrogen The One That Gets Protonated Chemhelp



Major And Minor Resonance Structures Organic Chemistry Socratic



Apexbio Guanidine Hcl
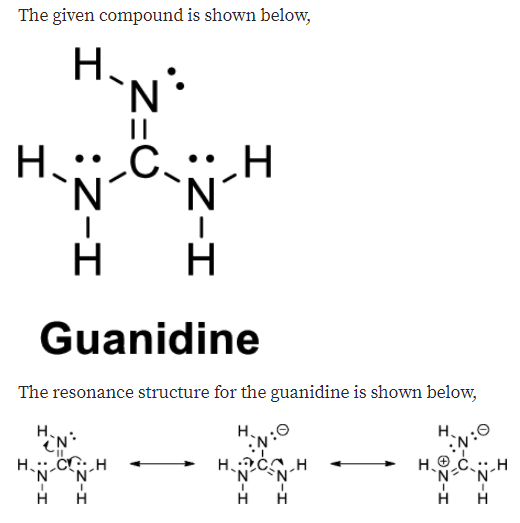



Answered Draw Three Contributing Structures Of Bartleby




Epb1 Methods For The Synthesis Of Polycyclic Guanidine Compounds Google Patents
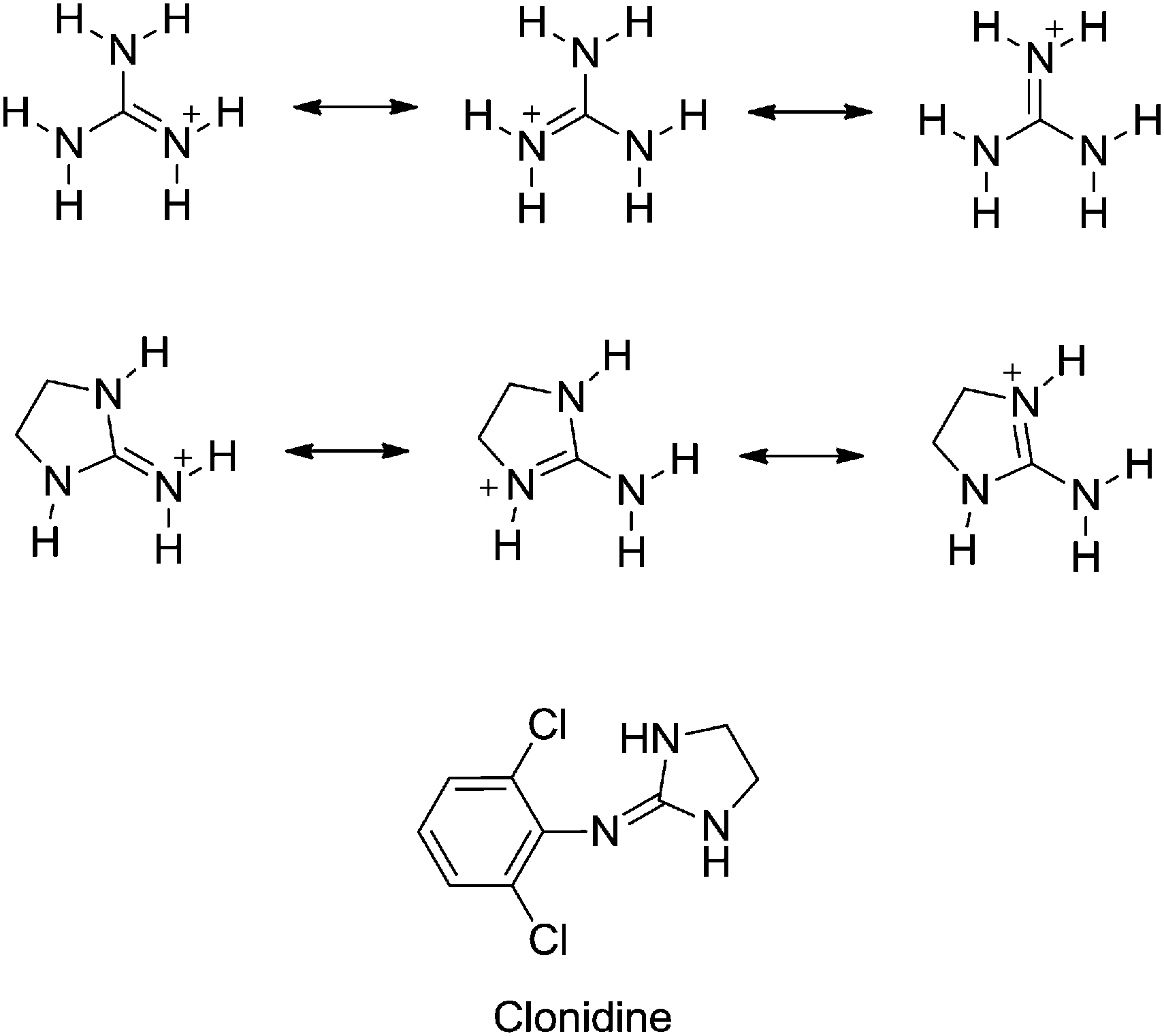



Substituent Effects On The Basicity P K A Of Aryl Guanidines And 2 Arylimino Imidazolidines Correlations Of Ph Metric And Uv Metric Values With P New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C7nje
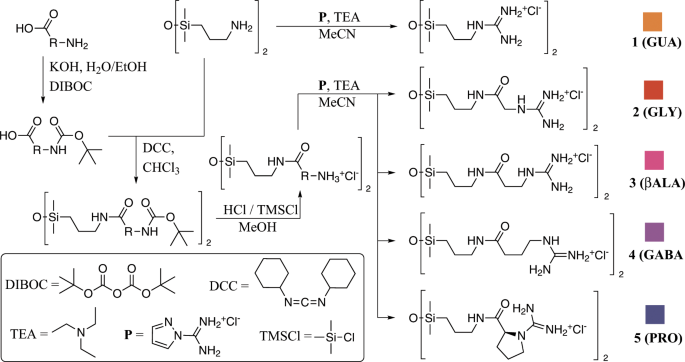



Exploring Ion Ion Preferences Through Structure Property Correlations Amino Acid Derived Bis Guanidinium Disiloxane Salts Scientific Reports




Study Of The Carbon Dioxide Chemical Fixation Activation By Guanidines Sciencedirect



Guanidine Thiocyanate Fumaric Acid Sodium Erythorbate Guanidine Carbonate Azodicarbonamide Sodium Dichloro Isocyanurate Azamethiphos Abtonsmart Chemicals Group Co Ltd
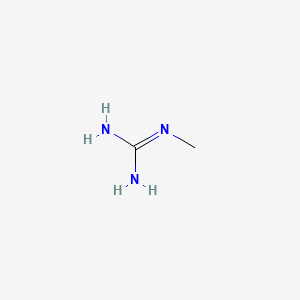



Methylguanidine C2h7n3 Pubchem



1




Resonance Delocalization In Bh Type Acids
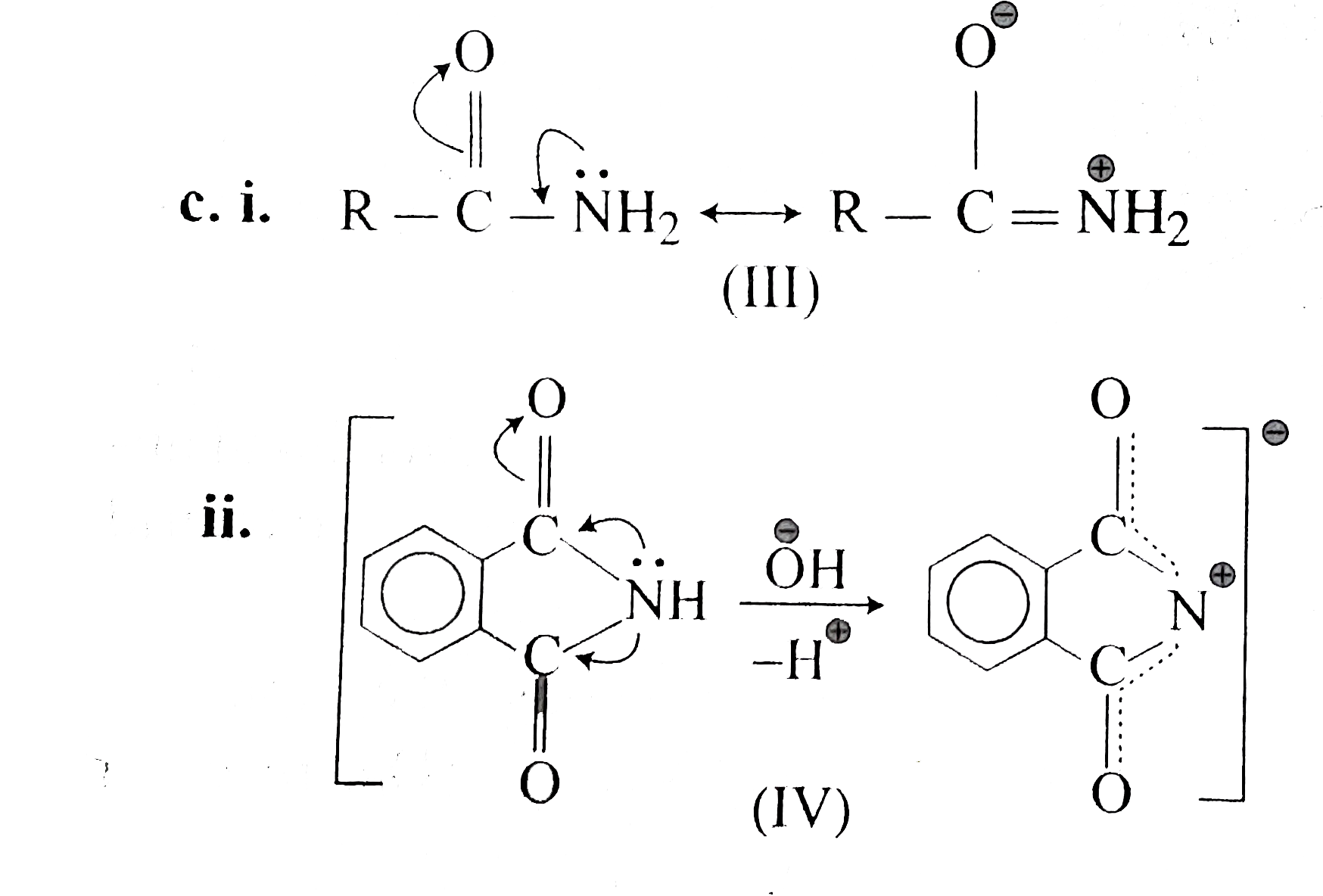



Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely To Be Protonated




Pdf Non Covalent Interactions Complexes Of Guanidinium With Dna And Rna Nucleobases Semantic Scholar




Zwitterion P Conjugated Network Polymer Based On Guanidinium And B Ketoenol As A Heterogeneous Organo Catalyst For Chemical Fixation Of Co2 Into Cyclic Carbonates Apl Materials Vol 7 No 11




Iit Jee Equivalent Resonance 2 Offered By Unacademy
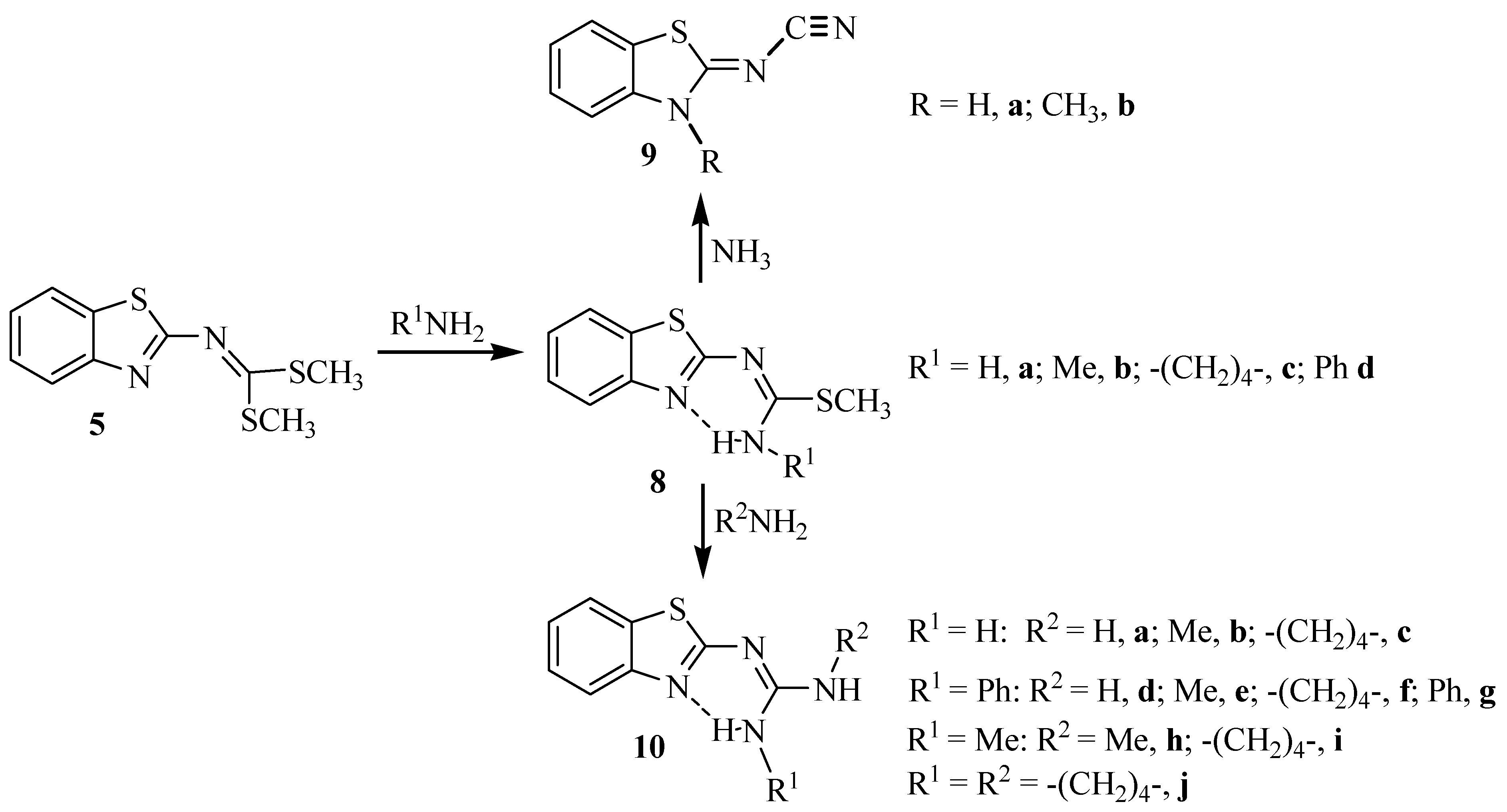



Molecules Free Full Text A Synthetic Method To Access Symmetric And Non Symmetric 2 N N Disubstituted Guanidinebenzothiazoles Html




Why There Is A Huge Difference Between The Basicity Of Urea And Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange


